Years ago, selling online was a lot like the wild west—no real rules or regulations. But today, the ecommerce industry is closely monitored and regulated by a wide range of local, regional, and national governing bodies. Ecommerce laws have been implemented to help protect consumers, businesses, and everyone else involved with ecommerce transactions.
To be clear, this guide does not constitute legal advice, and you should always consult with an attorney before making any decisions. But you can use the information below to help make sense of ecommerce laws and give yourself a baseline for compliance.
What is Ecommerce Law?
Ecommerce laws cover all regulations and legal issues related to the online sales industry. Any business that sells products or services online must comply with specific rules and regulations.
Failure to comply with ecommerce laws can result in lawsuits from consumers as well as fines and penalties from governing bodies.
Some ecommerce laws only apply to certain types of businesses and industries. For example, an ecommerce site that sells one particular product might not have to follow the same laws as another site selling a completely different product.
Other ecommerce laws are region specific. For example, GDPR compliance only applies to websites that serve users in the European Union. CCPA compliance only applies to consumers in California.
But there is also a wide range of ecommerce laws that everyone has to abide by, regardless of your industry, business location, or location of your customers.
Why Are Ecommerce Laws So Important?
Following the law is important for any business owner, including ecommerce sites. Understanding ecommerce laws will help protect yourself, protect your business, and protect your customers.
If you’re unknowingly breaking the law, it could have detrimental implications for your company. Aside from the hefty fines and legal penalties, you could potentially lose control over your brand reputation and assets.
Many ecommerce laws are set in place to help mitigate fraud, prevent identity theft, and keep consumer data safe.
Navigating the waters of ecommerce law can be tough for small and midsize businesses that don’t have a dedicated legal team. But ecommerce sites can rely on online legal services like Rocket Lawyer for assistance.

Rocket Lawyer gives you affordable access to legal advice from real attorneys. You’ll also have access to an extensive legal document library for things like privacy policies, terms and conditions pages, and other templates for staying compliant.
For new ecommerce sites that are just getting started, Rocket Lawyer can even help you set up an LLC or corporation—forming your business as a legal entity.
How Do I Comply With Ecommerce Tax Laws?
Taxation compliance is a huge part of ecommerce law.
Most ecommerce businesses need to pay taxes in multiple locations. First, your income is likely subject to US federal income taxes. You’ll also need to pay local state sales taxes, as well as other local city or county taxes.
Ecommerce operations are typically subject to taxes in the state where the business operates. But they’re also subject to taxes in states where they’re selling products and storing inventory.
For example, let’s say your business is based in Washington. But you have a warehouse of inventory in California, and you make an online sale to a customer in Texas. You’ll likely owe taxes in three different states.
To simplify your tax collection process, you can rely on tools to automate everything for you during checkout. Shopify has built-in tax management features that will automatically calculate the taxes owed on each transaction.

In addition to sales tax, you might also be responsible for import taxes. This typically applies to ecommerce businesses using international suppliers. If you buy in large quantities, you might even have to pay tariffs and other duties.
Many states have recently introduced environmental taxes to promote sustainability and protect the environment. For example, the California Redemption Value (CRV) regulatory fee mandates that consumers must pay $0.05 or $0.10 for recyclable plastic containers, depending on the size. But it’s the business’s responsibility to collect those taxes and file them appropriately.
Make sure you consult with a tax attorney to ensure your ecommerce business is compliant with all applicable tax laws.
How Do I Comply With Ecommerce Shipping Laws?
Certain types of products sold online are subject to different laws and regulations. This can sometimes be imposed at the state level, but it’s often handled by federal laws.
Ecommerce businesses that ship products across international borders must pay close attention to shipping laws as well.
Here are some examples of ecommerce products that could be restricted or have special laws regarding how they’re shipped:
- Firearms and ammunition
- Alcohol
- CBD products
- Perishable goods
- Fruits and vegetables
- Cigarettes and tobacco products
- Vape products
- Animals
- Aerosols
- Hazardous and poisonous materials
- Explosives
- Nail polish and perfumes
- Dry ice
- Airbags
- Live plants
Beyond shipping, some types of products are outright illegal to sell or possess in the United States. So while you might be able to sell certain pets online, you couldn’t legally operate an ecommerce business that sells forbidden exotic animals.
Are There Age Restrictions For Selling Products Online?
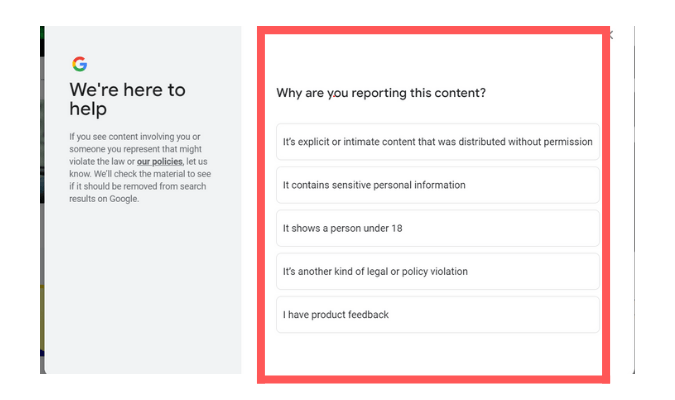
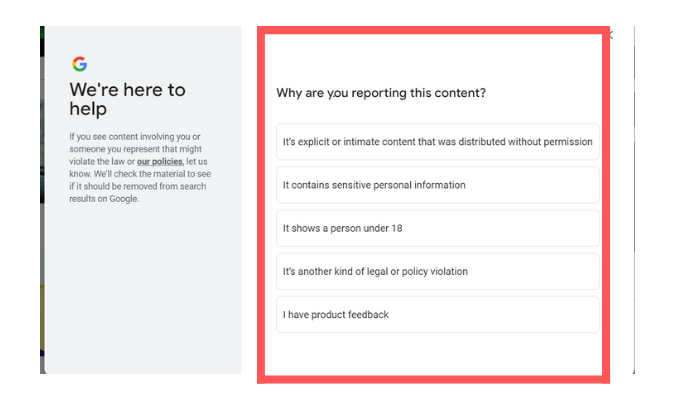
Every website, including ecommerce sites, must comply with COPPA (Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act). There are no exceptions to this law.
There are several requirements for COPPA compliance, but one that applies to many ecommerce sites has to do with data collection. You cannot collect any personal information of children under the age of 13. According to the regulation, websites can be liable for fines of up to $43,792 per violation.
You’ll also need to follow all state and federal laws for age-restricted products. For example, most states let you sell tobacco products to anyone who is 18 or older. But states like Tennessee and Wyoming restrict tobacco sales to anyone under 21 years old.
So even if you’re legally allowed to sell and ship tobacco products online, you’d have to make adjustments to ensure you’re only selling to people who are of age in the state you’re shipping to. Non-compliance in these situations would be handled at the state level.
What Trademark, Patent, and Copyright Laws Do Ecommerce Sites Need to Follow?
All trademarks, patents, and copyrights are protected by intellectual property laws. These rules and regulations are governed by the USPTO (United States Patent and Trademark Office).
Here’s a quick overview of each term:
- Trademark — Words, phrases, symbols, or designs to identify and distinguish the source of goods offered by one party from those of others.
- Patent — The right to an invention granted by the USPTO in exchange for public disclosure for a limited duration.
- Copyright — Protection of authorship, writings, music, and art that are tangibly expressed.
Legal jargon aside, there are two main takeaways for ecommerce sites when it comes to trademarks, patents, and copyright laws.
- You must take the appropriate steps to protect your own intellectual property.
- You cannot violate or infringe upon someone else’s intellectual property.
For example, you’re not allowed to print the Nike or Gucci logo on hats and sell them on your website. If you want to sell shirts with a Toy Story character on them, you’d need to obtain the rights of those characters from the appropriate party to avoid legal troubles.
LegalZoom is an excellent resource if you want to protect your ecommerce shop’s intellectual property.

You can also use it to run trademark, patent, and copyright searches to see if another business already owns the rights to something.
LegalZoom is also a great option to consider for other ecommerce law needs. You can use this online legal service to ask legal questions to attorneys at an affordable price.
Does My Ecommerce Site Need a Privacy Policy?
Privacy policies are legally required by law because ecommerce sites collect personal information from visitors and customers.
Personal data includes names, email addresses, shipping addresses, financial records, and anything else considered personally identifiable information.
Adding a privacy policy to your ecommerce site can help you stay compliant. Your privacy policy should clearly state exactly what type of information you’re collecting from visitors and how you’re using that information.
This should go without saying, but in addition to writing and publishing a privacy policy on your ecommerce site, ecommerce merchants must also abide by the terms that are set forth in those policies. So you can’t say you’re using customer data for one thing and then decide to use it for something else.
You can use platforms like Rocket Lawyer to obtain a privacy policy template.

Always have your attorney review and approve your privacy policy before you publish it online. But using a template is a great starting point, and it’s more affordable than having a lawyer draft your ecommerce privacy policy from scratch.
Does My Ecommerce Site Need to Have a Terms and Conditions Page?
A terms and conditions page acts as a contract between your ecommerce store and its visitors. These pages should contain a number of different clauses to legally protect your business throughout the entire sales process.
Some examples of what you should include on your terms and conditions page include:
- Liability limitations
- Return policy
- Latest consumer regulations
- Shipping timelines and delivery terms
- Jurisdictions
- Intellectual property
- Payment terms
- Dispute guidelines and process
The list goes on and on. This is definitely something that you’ll want to consult with an attorney about, as a boilerplate terms and conditions page likely won’t be sufficient for many ecommerce sites.
For example, if your product causes injury or bodily harm to a customer, your business might be liable if you don’t have an ironclad terms and conditions page. Even if you have terms and conditions published on your site, it doesn’t prevent customers from suing your business.
Does My Ecommerce Website Need to be PCI Compliant?
The Payment Card Industry (PCI) Data Security Standard (DSS) is a set of standards that were introduced by credit card companies back in 2004. The standards are often abbreviated as PCI DSS, or simplicity PCI.
While PCI compliance is not a federal or state law, it’s imposed by the card payments industry to ensure safe transactions for customers.
Failure to comply with PCI DSS could revoke your company’s ability to accept credit cards—which would be detrimental to an ecommerce website.
PCI compliance boils down to providing a safe and secure checkout environment for your customers online. Checkouts must be encrypted, and any cardholder data must be handled appropriately as well.
The easiest way to stay PCI compliant is by using a reputable payment gateway. Stripe is a great option to consider for ecommerce businesses.

It seamlessly integrates with all major ecommerce platforms, card networks, and banks.
If you have a secure ecommerce platform, credit card processor, and payment gateway, they’ll handle the PCI compliance for you. So you won’t have to worry about maintaining all of the technology behind the scenes to process transactions.
How Do Ecommerce Sites Comply With FTC Laws?
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has several laws that regulate how you’re marketing and advertising your ecommerce business and products online.
One key law that applies to ecommerce sites is the CAN-SPAM Act. This mandate was set forth to help prevent unsolicited emails. It also requires businesses to be honest and transparent with email marketing.
In short, you can’t market your products to people via email if they haven’t opted in to receive marketing messages. You must also give all of your email receptions the ability to opt out. If someone opts out of your marketing messages, you must honor those requests.
Even something like a marketing email with a deceptive subject line would be in violation of these laws.
Customer reviews are a key part of any ecommerce operation. Under the FTC’s Consumer Review Fairness Act, people have the right to share honest opinions about your products, services, and conduct on any forum. This includes third party review websites and social media.
Deceptive marketing tactics, false claims about your products, and fake reviews may also violate FTC laws. These are just a few examples, and you can visit the FTC’s website for more information.